Colonial Economies
(Lecture Notes from Mr. Kersey's 8th Grade U.S. History Class)Colonial Economies
- Each colony had an economic base, which is what people did to make their livings. Each place has a thing that they produced best.
- The West Indies: sugar and molasses.
- The Southern Colonies: tobacco, rice and indigo.
- New England Colonies: shipbuilding, slave trading, lumber, and fish.
- The Middle Colonies: shipbuilding, cattle, and grains.
- Great Britain: Manufactured goods.
- Britain would not pay cash (gold or silver) for things they bought, instead they would pay in goods. But, Britain would only accept cash for payment of taxes. So...
- ...this made cash very valuable in the Colonies. In fact, cash would become so valuable it drove down the prices of Colonial goods. Colonists would sell goods for unfairly small amount of cash because they were desperate to have it.
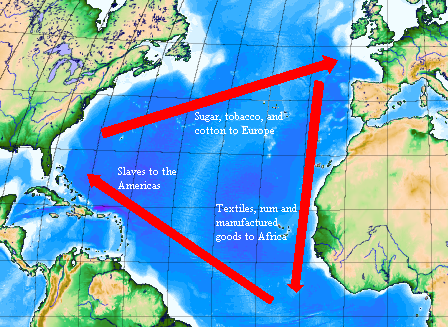
Triangular Trade
- Colonial merchants were able to get gold and silver by working around the Navigation Acts with something called the Triangular Trade.
- Tobacco is sold in England in exchange for Manufactured Goods.
- Manufactured Goods are sold for cash in Africa and Slaves are bought.
- Slaves are sold in Virginia for cash and Tobacco is bought.
- Each time goods are sold for a cash profit, the Colonial merchant was able to make a bit of gold and silver. When goods were swapped in Britain, that was OK because they could sell these goods for cash elsewhere.