Multiple Choice
Identify the
choice that best completes the statement or answers the question. Some names have alternate
spellings, so be alert. Good luck, and may the Force be with you!
|
|
|
1.
|
Where is the Arabian Peninsula located?
a. | the northwest corner of Asia | c. | the northeast corner of
Asia | b. | the southeast corner of Asia | d. | the southwest corner of
Asia |
|
|
|
2.
|
Why do geographers call Arabia a “crossroads” location?
a. | It is home to very few cultures or people. | b. | Trade routes linking
Africa, Asia, and Europe run through it. | c. | People from many different cultures live
there. | d. | It is where Islam, Christianity, and Judaism started. |
|
|
|
3.
|
Which physical feature dominates the landscape of Arabia?
a. | marshy land | c. | fertile oases | b. | sandy deserts | d. | large mountains |
|
|
|
4.
|
A nomad was a person who
a. | traveled from place to place. | c. | sold cooking supplies and
clothing. | b. | farmed and raised animals. | d. | settled in an oasis. |
|
|
|
5.
|
In terms of importance to Arabian nomads, which concern would you rank
first?
a. | getting food and water for their animals | b. | finding shelter for
themselves | c. | visiting oases frequently | d. | making deals with traders for
supplies |
|
|
|
6.
|
| But as Muhammad was growing up, many rich merchants began to ignore the poor and keep their
wealth for themselves. | |
In what way did Muhammad react to these changes? a. | He became concerned but did nothing about them. | b. | He went on a
pilgrimage to the shrine in Mecca. | c. | He prayed and meditated in the hills outside
Mecca. | d. | He left Mecca and traveled to Jerusalem. |
|
|
|
7.
|
Which of the following events happened first?
a. | Muhammad began to tell people about messages from God. | b. | Muhammad taught that
there was only one God. | c. | Muhammad received messages from God through an
angel. | d. | Muhammad meditated in a cave outside Mecca. |
|
|
|
8.
|
What was the most important difference between Muhammad’s teachings and
the beliefs of other Arabs?
a. | Muhammad taught that people should be kind to the poor. | b. | Muhammad taught that
there was only one God. | c. | Muhammad taught that there were many
gods. | d. | Muhammad taught that people should make pilgrimages to
Kaaba. |
|
|
|
9.
|
What did the early followers of Islam, Judaism, and Christianity all have in
common?
a. | They all believed that Muhammad was a prophet. | b. | They all believed
that Jesus was the son of God. | c. | They all believed that there were many
gods. | d. | They all believed that there was only one God. |
|
|
|
10.
|
Before they heard Muhammad’s teachings, many Arabs visited the Kaaba in
Mecca each year to
a. | worship their gods. | c. | trade at its large marketplace. | b. | give money to the
poor of Mecca. | d. | show their
devotion to Islam. |
|
|
|
11.
|
Which of the following best summarizes how Muhammad’s teachings affected
the people of Arabia?
a. | The teachings made people want to be merchants. | b. | The teachings had
very little effect on the people. | c. | The teachings made people turn to
Christianity. | d. | The teachings challenged and upset many people. |
|
|
|
12.
|
In what way is the Qur´an similar to holy books of other religions?
a. | It describes guidelines for moral behavior. | b. | It states that Islam
is the true religion. | c. | It prohibits owning slaves. | d. | It describes the
life of Muhammad. |
|
|
|
13.
|
Which of the following is the central teaching of Islam?
a. | Allah will grant life in paradise to all who obey him. | b. | Allah is the only
God and Muhammad is his prophet. | c. | On the final day Allah will judge all
people. | d. | Muslims must wash before praying to be pure before
Allah. |
|
|
|
14.
|
All of the following are rules described in the Qur´an except
a. | Muslims may not drink alcohol. | c. | Muslims must wash before
praying. | b. | Muslims may not eat pork. | d. | Muslims must ignore the hadith. |
|
|
|
15.
|
Which of the following is not an Islamic belief?
a. | Moses was a prophet. | c. | Allah is the only God. | b. | Muhammad was the son
of God. | d. | Abraham was a
prophet. |
|
|
|
16.
|
The Sunnah is based on the
a. | hadith. | c. | Qur´an. | b. | Shariah. | d. | Five Pillars of
Islam. |
|
|
|
17.
|
Which of the following best summarizes the Five Pillars of Islam?
a. | They are stories about the life of Muhammad. | b. | They are the basis
for law in Muslim countries. | c. | They are acts of worship required of all
Muslims. | d. | They are rules about how Muslims should treat others. |
|
|
|
18.
|
Which of the following can you infer from the fifth pillar of Islam?
a. | Other religions do not require their believers to fast. | b. | Mecca is important
to Muslims. | c. | Muhammad’s home was in Medina. | d. | There are no cities that are holy to
Islam. |
|
|
|
19.
|
Which of the following best describes why Islamic law is important to
Muslims?
a. | It helps people live according to their religious values. | b. | It says what Muslims
should not eat or drink. | c. | It is a written record of the life of
Muhammad. | d. | It is one of the Five Pillars of Islam. |
|
|
|
20.
|
The Qur´an and the Sunnah both form the basis for
a. | the hadith. | c. | Islamic law. | b. | the hajj. | d. | jihad. |
|
|
|
21.
|
After Muhammad’s death, the title given to Islam’s highest leaders
was
a. | successor. | c. | sultan. | b. | caliph. | d. | emperor. |
|
|
|
22.
|
Which area was conquered by the Muslims last?
a. | the Persian Empire | c. | North Africa | b. | the Byzantine Empire | d. | Spain |
|
|
|
23.
|
Muslims showed tolerance by
a. | accepting other people’s religious beliefs. | b. | converting others to
Islam. | c. | allowing only Christians to practice their religion. | d. | conquering the
Berbers. |
|
|
|
24.
|
In what way were Córdoba and Baghdad similar?
a. | They were both located in what is now Iraq. | b. | They both had public
water and lighting systems. | c. | They were both centers of culture and
learning. | d. | They both exported valuable textiles and jewelry. |
|
|
|
25.
|
What was the most important factor in the spread of Islam during the
600s?
a. | trading with non-Muslims | c. | translating Arabic texts into
Latin | b. | producing Islamic art | d. | conquering non-Muslims |
|
|
|
26.
|
What was the result of the exchange of beliefs and customs between Muslims and
the people they conquered?
a. | Islam became less popular. | b. | Different cultures blended
together. | c. | The Muslim Empire decreased in size. | d. | Trade became less
important. |
|
|
|
27.
|
In what way were the effects of trade and tolerance on the Muslim world
similar?
a. | They both allowed other cultures to influence the Muslim world. | b. | They both made new
products available to Muslims. | c. | They both caused Muslims to ignore the
influence of other cultures. | d. | They both caused Islam to stop
spreading. |
|
|
|
28.
|
Which Ottoman leader became known as “the Conqueror”?
a. | Suleyman I | c. | Esma’il | b. | Mehmed II | d. | ´Abbas |
|
|
|
29.
|
During Suleyman I’s rule, the Ottoman Empire
a. | took control of the Eastern Mediterranean and parts of Europe. | b. | defeated the
Byzantine Empire. | c. | turned the Hagia Sophia church into a
mosque. | d. | expanded into Anatolia and conquered Syria and Egypt. |
|
|
|
30.
|
Which of the following best describes the Ottoman Empire between 1453 and
1566?
a. | It greatly expanded its power and territories. | b. | It lost many battles
and territories. | c. | It became too large to be ruled from the capital. | d. | It united all of the
Muslim empires. |
|
|
|
31.
|
Akbar’s tolerant religious policy helped
a. | convert more people to Islam. | b. | unify the Mughal Empire. | c. | end the warfare
between Hindus and Muslims. | d. | establish the Mughal Empire in
1526. |
|
|
|
32.
|
Which of the following best describes how the Ottoman Empire and the Mughal
Empire were similar?
a. | They both were blends of different cultures. | b. | They both encouraged
people to learn Urdu. | c. | They both were made up of Turkish
Muslims. | d. | They both made Shiism their official religion. |
|
|
|
33.
|
Which of the following is true of the Ottoman, Safavid, and Mughal
empires?
a. | They were ruled by leaders called shahs. | b. | They practiced
religious tolerance throughout their entire history. | c. | They tried to expand their territory through
warfare. | d. | They wanted to convert other Muslims to Shiism. |
|
|
|
34.
|
In terms of importance to the spread of knowledge in the Islamic world, which
would you rank first?
a. | The scholars made advances in math and science. | b. | The scholars spoke
different languages. | c. | The scholars came from different
cultures. | d. | The scholars all understood Arabic. |
|
|
|
35.
|
Muslim calligraphy was a combination of
a. | science and mathematics. | c. | art and
science. | b. | art and religion. | d. | astronomy and geography. |
|
|
|
36.
|
Minarets were used to
a. | store Islamic texts. | c. | call Muslims to prayer. | b. | hold translations of
poetry. | d. | decorate
mosques. |
|
|
|
37.
|
Which of the following is true of Muslim art and architecture?
a. | They became more important than religion in the Muslim world. | b. | Muslims were only
interested in them if they helped spread Islam. | c. | They were both influenced in some way by the
Muslim religion. | d. | Islam would not have spread without them. |
|
|
|
PRACTICING SOCIAL STUDIES SKILLS
Study the information below and
answer the question that follows.
|
|
|
38.
|
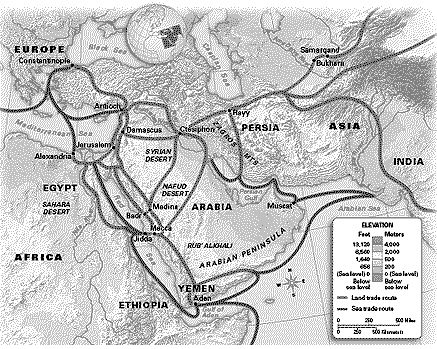 What can you infer about the journey from
Ctesiphon to Medina? a. | It was slower than a journey from Ctesiphon to Mecca. | b. | People who made the
trip were very wealthy. | c. | It was a difficult journey through a harsh
climate. | d. | People did not take this route because it was too
dangerous. |
|
|
|
39.
|
 What is one activity that monks probably
did? a. | riding horses | c. | ruling territories | b. | bartering goods | d. | reading and
writing |
|
|
|
40.
|
 On which point did Pope Gregory VII and
Emperor Henry IV agree? a. | Bishops should decide who would be the emperor. | b. | Priests should be
considered more powerful than kings. | c. | Kings should have more influence over the
churches than priests. | d. | Bishops should be chosen by the leader whose
power came from God. |
|
|
|
41.
|
 What did Machiavelli think about people in
general? a. | They are greedy. | c. | They are loyal to what they love. | b. | They want to be
loved. | d. | They want rulers
they are afraid of. |
|
|
|
42.
|
Which geographic feature covers most of southern Europe?
a. | forests | c. | plains | b. | mountains | d. | lakes |
|
|
|
43.
|
Because northern Europeans lived on rich, fertile plains, they
a. | farmed a variety of crops. | c. | raised sheep and
goats. | b. | grew grapes and olives. | d. | planted many trees and shrubs. |
|
|
|
44.
|
The geography and climates of northern and southern Europe caused
a. | both areas to develop similar ways of life. | b. | each area to build
cities on islands for protection. | c. | both areas to develop a feudal
system. | d. | each area to develop a different way of life. |
|
|
|
45.
|
How did the peninsulas of southern Europe affect the way people lived?
a. | People on the peninsulas raised goats and sheep. | b. | People on the
peninsulas grew grapes and olives. | c. | People on the peninsulas became great seafarers
and traders. | d. | People on the peninsulas became farmers. | e. | People built
undersea fortresses defended by sea monsters. |
|
|
|
46.
|
Southern Europe was invaded by raiders less often than northern Europe because
it had more
a. | mountains. | c. | peninsulas. | b. | rivers. | d. | plains. |
|
|
|
47.
|
Which element of European geography contributed to the development of
feudalism?
a. | the rivers, which allowed the Vikings to attack inland cities | b. | the mountains, which
prevented Viking raids | c. | the ocean, which prevented attacks from the
west | d. | the forests, which allowed raiders to move secretly |
|
|
|
48.
|
The people who were most important in spreading Christianity throughout Europe
were
a. | the monks, missionaries, and knights. | b. | Saint Benedict, Saint Patrick, and the
monks. | c. | Saint Patrick, Saint Benedict, and Charlemagne. | d. | the popes,
missionaries, and monks. |
|
|
|
49.
|
Saint Patrick
a. | was an Italian monk from the 500s. | b. | converted the Irish to
Christianity. | c. | created rules for how monks should live. | d. | helped Charlemagne
conquer parts of Europe. |
|
|
|
50.
|
Monks and missionaries were similar in that they both
a. | traveled to spread Christian teachings. | b. | lived apart from
society in isolated communities. | c. | followed the guidelines of Saint
Benedict. | d. | helped spread Christian teachings to new areas. |
|
|
|
51.
|
Which of the following was not a way in which monks contributed to medieval
society?
a. | running schools | c. | serving as scribes to rulers | b. | collecting ancient
writings | d. | defending the
pope |
|
|
|
52.
|
Who built a European empire and was crowned Emperor of the Romans in 800?
a. | Clovis | c. | Pope Leo III | b. | Saint Patrick | d. | Charlemagne |
|
|
|
53.
|
What can you infer about Charlemagne from his accomplishments?
a. | He was interested in spreading feudalism. | b. | He was not very
concerned with education. | c. | He did not think religion was
important. | d. | He wanted to gain great power in Europe. |
|
|
|
54.
|
In what way were Charlemagne’s empire and the old Roman Empire
similar?
a. | Neither gained new territory through warfare. | b. | Both existed during
the 700s and 800s. | c. | Neither was governed by a Christian
ruler. | d. | Both included large parts of Europe. |
|
|
|
55.
|
The invaders from Scandinavia who attacked Europe during the 700s and 800s were
called
a. | Vikings. | c. | samurai. | b. | Muslims. | d. | Magyars. |
|
|
|
56.
|
The Viking, Magyar, and Muslim invasions of Europe directly caused the
development of the
a. | manor system. | c. | Benedictine rules. | b. | code of chivalry. | d. | feudal system. |
|
|
|
57.
|
Which of the following is the best prediction of what might have happened if the
Vikings had not invaded Europe?
a. | Knights would have been unable to find work to do. | b. | Nobles would not
have needed knights to protect them. | c. | Serfs would not have been needed to farm the
lands of nobles. | d. | Peasants would have been hired to protect the lands of
nobles. |
|
|
|
58.
|
What did knights receive in exchange for their pledge of loyalty to a
lord?
a. | a weapon | c. | an income | b. | a fief | d. | a title |
|
|
|
59.
|
The main duty of a vassal was to
a. | run his lord’s estate. | c. | farm land owned by
nobles. | b. | advise the king. | d. | fight to defend his lord’s land. |
|
|
|
60.
|
Feudalism began to spread to Britain soon after
a. | Charlemagne was crowned Emperor of the Romans. | b. | the Vikings began
raiding northern Europe. | c. | William the Conqueror invaded
Britain. | d. | Eleanor of Aquitaine married King Henry II of
England. |
|
|
|
61.
|
A manor was a large estate owned by a
a. | knight or lord. | c. | peasant or farmer. | b. | knight or peasant. | d. | daimyo or
samurai. |
|
|
|
62.
|
The manor system evolved because
a. | new technology increased the size of harvests. | b. | knights could not
work their own fields. | c. | the population in Europe
increased. | d. | rocky terrain in southern Europe made farming
difficult. |
|
|
|
63.
|
Which best summarizes the manor system?
a. | Lords gave land to peasants for them to farm. | b. | Vassals pledged
loyalty to one or more lords. | c. | Lords gave fiefs to knights in exchange for
protection. | d. | Serfs farmed lands owned by lords. |
|
|
|
64.
|
Which of the following best summarizes how feudalism reached Britain?
a. | William the Conqueror conquered England and rewarded his knights with land
there. | b. | Frankish knights introduced feudalism to Britain in the 1000s. | c. | Charlemagne made
Britain part of his empire and established feudalism there. | d. | Eleanor of Aquitaine
married King Louis VII of England and moved her vassals there. |
|
|
|
65.
|
Which of the following happened after Europe’s population began to
increase during the Middle Ages?
a. | Feudalism increased. | c. | Feudalism declined. | b. | The manor system spread. | d. | Trade
decreased. |
|
|
|
66.
|
The growth of European cities around the year 1000 was caused by
a. | the increase of population and trade. | c. | the end of the manor
system. | b. | the decrease of Viking raids. | d. | the spread of
Christianity. |
|
|
|
67.
|
What was the most important similarity between knights and samurai?
a. | They received land for their service. | b. | They both pledged loyalty to
lords. | c. | They practiced the same religion. | d. | They both had peasants working their
lands. | e. | Neither could use The Force, like Jedi Knights. |
|
|
|
68.
|
Samurai warriors and European knights both followed codes of behavior that
emphasized
a. | personal fulfillment. | c. | respect for nature. | b. | loyalty. | d. | vengeance. |
|
|
|
69.
|
During the Middle Ages, power in Europe shifted from nobles to
a. | knights and peasants. | c. | kings and popes. | b. | merchants and traders. | d. | monks and
priests. |
|
|
|
70.
|
All of the following were duties and powers of popes during the Middle Ages
except
a. | deciding when someone was acting against the church. | b. | writing letters to
explain religious teachings. | c. | providing guidance on how to live and
pray. | d. | forging treaties with religious leaders of other
regions. |
|
|
|
71.
|
Medieval Christians feared excommunication because they believed that
a. | those cast out from the church had to leave their village. | b. | those cast out from
the church would not get into heaven. | c. | those cast out from the church could not get
work. | d. | those cast out from the church could not own
property. |
|
|
|
72.
|
Which leader benefited from cooperating with the pope?
a. | Emperor Henry IV | c. | William the Conqueror | b. | the bishop of
Constantinople | d. | Charlemagne |
|
|
|
73.
|
A split in the Christian Church started in the 1000s because
a. | people in western Europe refused to recognize the authority of the
pope. | b. | some bishops were selected by kings while some were named by the
pope. | c. | bishops in eastern Europe refused to recognize the authority of the
pope. | d. | some kings encouraged strict adherence to the faith while some did
not. |
|
|
|
74.
|
As popes tried to increase their power, they came into conflict with
a. | kings. | c. | bishops. | b. | nobles. | d. | invaders. |
|
|
|
75.
|
Pope Gregory VII and Emperor Henry IV disagreed about
a. | how serfs and peasants should be treated in feudal society. | b. | who should select
bishops. | c. | where in Europe the church headquarters should be located. | d. | who could
excommunicate people. |
|
|
|
76.
|
Why were the Crusades fought?
a. | to bring the eastern bishops back under the pope’s control | b. | to protect European
territory from invading Muslims | c. | to unite the Roman Catholic Church and the
Eastern Orthodox Church | d. | to gain control of Jerusalem (Palestine), the
Holy Land |
|
|
|
77.
|
During the Crusades, Christians fought against
a. | Muslims. | c. | the Byzantine Empire. | b. | Germans. | d. | other Christians. |
|
|
|
78.
|
Which of the following happened first?
a. | Peasant Crusaders attacked Jews in Germany. | b. | Saladin successfully
defended Jerusalem against King Richard I. | c. | Crusaders attacked
Constantinople. | d. | Pope Urban II called on Christians to fight the Muslim
Turks. |
|
|
|
79.
|
The Byzantine emperor asked the pope for help because
a. | Muslim Turks threatened Constantinople. | b. | tension between
Christians and Jews was growing. | c. | Muslim Turks captured
Jerusalem. | d. | Europeans had been attacked in the Holy Land. |
|
|
|
80.
|
What was the outcome of the Crusades?
a. | The Holy Land came under Christian control. | b. | The Holy Land
remained under Muslim control. | c. | The Holy Land was destroyed and
abandoned. | d. | The Holy Land was divided by the two sides. |
|
|
|
81.
|
One reason Christian Crusaders lost the Holy Land was that
a. | they didn’t have the support of the Eastern Orthodox
Church. | b. | they didn’t understand the reason for the conflict. | c. | they lacked support
from kings and nobles. | d. | they traveled long distances to the
battles. |
|
|
|
82.
|
Which of the following occurred as a result of the Crusades?
a. | Contact between Jews, Christians, and Muslims was peaceful. | b. | Feudalism spread to
Asia and Northern Africa. | c. | Trade between Europe and Asia
increased. | d. | Kings became less powerful. |
|
|
|
83.
|
After the Crusades, the Byzantines distrusted western Christians because
a. | the Christians had attacked Jews. | b. | the Turks attacked the Byzantine
Empire. | c. | the Crusaders sacked Constantinople. | d. | Pope Urban II did not send them
help. |
|
|
|
84.
|
What was the most important result of the Crusades?
a. | European kings increased their power. | b. | Popes increased their
power. | c. | Muslims and Christians gained respect for one another. | d. | Trade and exchange
of ideas between Europe and Asia increased. |
|
|
|
85.
|
In medieval society, markets, festivals, and religious ceremonies took place at
a
a. | manor house. | c. | local church. | b. | monastery. | d. | university. |
|
|
|
86.
|
What is a pilgrim?
a. | a person who journeys to a religious location | b. | a person who works
to convert people to Christianity | c. | a clergy member who lives with the general
public | d. | a clergy member who takes a vow of silence |
|
|
|
87.
|
Where did friars live?
a. | monasteries | c. | universities | b. | villages | d. | churches |
|
|
|
88.
|
How were the lives of friars different from the lives of monks?
a. | Monks were teachers; friars were not. | b. | Friars were allowed to marry; monks were
not. | c. | Friars lived with the general public; monks lived apart in
monasteries. | d. | Monks lived in monasteries; friars lived in convents. |
|
|
|
89.
|
Who played the biggest role in creating the first universities in Europe?
a. | Muslim scholars | c. | noble landowners | b. | kings and queens | d. | church leaders |
|
|
|
90.
|
Which of the following best explains why Gothic cathedrals were symbols of
Christian faith?
a. | They were filled with beautiful objects. | c. | They were taller than other
churches. | b. | They were towering and majestic. | d. | Bishops held services
there. |
|
|
|
91.
|
Which of the following is a characteristic of Gothic cathedrals?
a. | high ceilings | c. | small altars | b. | plain windows | d. | central domes |
|
|
|
92.
|
Most art and architecture created in the Middle Ages was
a. | inspired by the lives of kings. | c. | created by clergy
members. | b. | based on natural law. | d. | concerned with religious expression. |
|
|
|
93.
|
Why did nobles make King John sign Magna Carta in 1215?
a. | They wanted to assert the authority of the pope. | b. | They wanted to
separate church and state. | c. | They wanted to replace him with a different
ruler. | d. | They wanted to limit the king’s power. |
|
|
|
94.
|
The English did all of the following to protect their rights except
a. | create a council called Parliament. | b. | abolish the monarchy. | c. | free the court
system of the king’s control. | d. | require everyone to obey the
law. |
|
|
|
95.
|
What started the Hundred Years’ War?
a. | Muslims invaded Europe. | b. | The Holy Roman Empire
split. | c. | The king of England invaded France. | d. | The pope had a fight with the king of
France. | e. | The Rebels blew up the Death Star. |
|
|
|
96.
|
France won the Hundred Years’ War because of the efforts of
a. | Pope Leo IX. | c. | Queen Isabella. | b. | King John. | d. | Joan of Arc. |
|
|
|
97.
|
In what way was England different from France after the Hundred Years’
War?
a. | The English king lost power while the French king gained power. | b. | England’s
population was smaller than that of France. | c. | English peasants went to cities while French
peasants remained in the country. | d. | The English converted to Protestantism while
the French remained Roman Catholic. |
|
|
|
98.
|
People caught the Black Death through contact with
a. | rats. | c. | fleas. | b. | flies. | d. | birds. |
|
|
|
99.
|
From 1347 to 1351, the plague
a. | spread from Europe to Asia. | c. | stayed confined to western
Europe. | b. | strengthened the manor system. | d. | reduced Europe’s population by a
third. |
|
|
|
100.
|
How did life change for surviving peasants and serfs after the plague?
a. | They began to demand wages for their labor. | b. | They moved from
towns to the country. | c. | They had to work much longer
days. | d. | They took over the manors. |
|
|
|
101.
|
Whose rule in Spain ended in 1002?
a. | the pope’s | c. | Jewish elders’ | b. | the French king’s | d. | Muslim
Moors’ |
|
|
|
102.
|
The marriage of Isabella and Ferdinand
a. | united France and England. | c. | united Castile and
Aragon. | b. | united Moors and Christians. | d. | united Jews and
Christians. |
|
|
|
103.
|
The main goal of Queen Isabella and King Ferdinand was to
a. | conquer land in France. | b. | make the pope recognize their
authority. | c. | end feudalism throughout their territory. | d. | make all of Spain
Christian. |
|
|
|
104.
|
What was the purpose of the Spanish Inquisition?
a. | to expel all Muslim spies from the country | b. | to reveal and stop
church corruption and waste | c. | to punish and kill heretics and non-Christians
in Spain | d. | to find and burn places afflicted with the plague |
|
|
|
105.
|
During the Middle Ages, Jews
a. | were discriminated against throughout Europe. | b. | controlled territory
in much of Europe. | c. | had a strong alliance with
Muslims. | d. | began several important universities. |
|
|
|
106.
|
Which of the following describes one effect of Marco Polo’s journey to
China?
a. | Marco Polo became the emperor of Japan. | b. | Marco Polo was made
a government official in China. | c. | Marco Polo helped protect travelers and traders
on the trade route to China. | d. | Marco Polo became an important
banker. |
|
|
|
107.
|
Venice was famous for
a. | producing silk cloth. | c. | manufacturing woolen cloth. | b. | manufacturing
weapons. | d. | producing
glass. |
|
|
|
108.
|
The Mongols helped increase trade between Europe and Asia by
a. | staying isolated from people from other countries. | b. | increasing the
prices of goods. | c. | making the Silk Road safe to travel again. | d. | building ports and
harbors. |
|
|
|
109.
|
One important feature that Venice and Genoa shared was that
a. | both were located near the Silk Road. | b. | both were important port cities on the
Mediterranean Sea. | c. | both produced fine glass, weapons, and
silk. | d. | both were centers of learning during the Middle Ages. |
|
|
|
110.
|
Which event occurred first?
a. | Marco Polo and his family travel from Venice to China. | b. | Marco Polo visits
India and Southeast Asia. | c. | Kublai Khan appoints Marco Polo to be a
government official. | d. | The Mongol dynasty takes over China and makes
the roads safer. |
|
|
|
111.
|
Which of the following best describes Cosimo de´ Medici?
a. | a wealthy merchant who supported the arts | b. | a ruler of the Papal
States | c. | a Renaissance scientist who helped build the foundations of modern
astronomy | d. | a powerful ruler of Florence who valued education and
culture |
|
|
|
112.
|
How do prices affect trade?
a. | When prices are low, trade decreases. | b. | When prices are high, trade does not
change. | c. | When prices are high, trade increases. | d. | When prices are low, trade
increases. |
|
|
|
113.
|
Which of the following ideas was not part of humanism?
a. | Ancient Greek and Roman writings were sources of inspiration. | b. | The only purpose of
art was to glorify God. | c. | Poetry, history, and public speaking were
important subjects to study. | d. | Talented writers and artists were
honored. |
|
|
|
114.
|
What effect did the merchant families have on the Renaissance in Italian
cities?
a. | The families wanted everyone to see what their money could buy. | b. | The families used
their wealth to keep the trade routes safe. | c. | The families supported the work of scientists
and mathematicians. | d. | The families supported arts and
learning. |
|
|
|
115.
|
What did Dante and Desiderius Erasmus have in common?
a. | Both were members of the clergy. | b. | Both had studied ancient classical
writings. | c. | Both wrote about problems they observed in their societies. | d. | Both lived in
Northern Europe. |
|
|
|
116.
|
Machiavelli wanted to have an effect on
a. | religion. | c. | art. | b. | politics. | d. | literature. |
|
|
|
117.
|
How are classical and Renaissance statues alike?
a. | Both feature figures with clothing that is still and without
motion. | b. | Both focus on animal figures. | c. | Both feature a few details of human
figures. | d. | Both feature realistic and lifelike poses. |
|
|
|
118.
|
What was the most important feature of humanism in northern Europe?
a. | The art of northern Europe showed people working in fields. | b. | Objects were painted
clearly. | c. | Artists showed physical flaws. | d. | Scholars combined humanist and religious
ideas. |
|
|
|
119.
|
Which word best summarizes the Renaissance?
a. | perspective | c. | change | b. | astronomy | d. | monarchy |
|
|
|
120.
|
Miguel de Cervantes is best known for
a. | Romeo and Juliet. | c. | the Sistine Chapel. | b. | Don Quixote. | d. | the Mona Lisa. |
|
|
|
121.
|
The printing press affected the spread of ideas during the Renaissance the same
way that
a. | the Internet affects the spread of ideas today. | b. | the cellular phone
affects the spread of ideas today. | c. | digital photographs affect the spread of ideas
today. | d. | e-mail allows people to exchange ideas today. |
|
|
|
122.
|
In what way did Desiderius Erasmus differ from Martin Luther?
a. | Erasmus published his ideas. | b. | Erasmus praised the work of church
officials. | c. | Erasmus founded the Jesuit order. | d. | Erasmus did not break completely from the
Catholic Church. |
|
|
|
123.
|
People supported Martin Luther because
a. | they were also unhappy with church practices. | b. | they wanted to read
the Bible in German. | c. | Luther gave out free
indulgences. | d. | Luther was a popular priest in Wittenberg. |
|
|
|
124.
|
The Catholic Church tried to prevent the spread of Protestantism in all of these
ways except
a. | by seeking out and punishing Protestants. | b. | by allowing Jesuits
to use weapons against Protestants. | c. | by creating new religious orders to spread
Catholic teachings. | d. | by banning books written by Protestant
leaders. |
|
|
|
125.
|
Which three words best describe what took place at the Council of Trent?
a. | service, discipline, education | b. | discussion, debate, reform | c. | investigation,
response, excommunication | d. | predestination, self-government,
federalism |
|
|
|
126.
|
Which statement best summarizes the Catholic Reformation?
a. | The Catholic Church adopted much-needed changes. | b. | The Jesuits started
schools for Catholic children. | c. | The church officially rejected the ideas set
out by Martin Luther. | d. | Bishops had to live in the areas they served,
and priests had to stop selling indulgences. |
|
True/False
Indicate whether the
statement is true or false.
|
|
|
127.
|
Arabia lies in a cool, wet region of the world.
|
|
|
128.
|
Belonging to a tribe probably gave nomads better access to grazing land.
|
|
|
129.
|
The caravan trade business made many people in Mecca rich.
|
|
|
130.
|
Mecca’s rulers approved of Muhammad’s teachings and helped spread
the Islamic message.
|
|
|
131.
|
Muhammad was a local merchant in Mecca before he became known for the
introduction of Islam.
|
|
|
132.
|
Many merchants in Mecca rejected the teachings of Muhammad because they did not
want to lose money.
|
|
|
133.
|
Muslims believe that God spoke to Muhammad through an angel.
|
|
|
134.
|
Muslims consider the Shariah to be the exact word of God as it was told to
Muhammad.
|
|
|
135.
|
Muslims study the hadith, which is a written record of Muhammad’s words
and actions.
|
|
|
136.
|
The Kaaba is Islam’s most sacred place.
|
|
|
137.
|
Qur´an is another name for Islamic law.
|
|
|
138.
|
The Qur´an and the Shia guide Muslims in their daily life.
|
|
|
139.
|
Muslims forced those they conquered to convert to Islam.
|
|
|
140.
|
The Ottoman, Safavid, and Mughal were formed as Islamic empires after the spread
of Islam.
|
Matching
|
|
|
Match each item with the correct statement. a. | medieval | h. | missionaries | b. | monks | i. | fiefs | c. | roles | j. | monasteries | d. | peasant | k. | chivalry | e. | manor | l. | vassal | f. | serf | m. | Clovis | g. | Henry
II |
|
|
|
141.
|
the Latin word for “Middle Age”
|
|
|
142.
|
People who try to convert others to a particular religion
|
|
|
143.
|
Religious men who lived apart from society
|
|
|
144.
|
Communities of monks
|
|
|
145.
|
King under whose rule the Franks became Christian
|
|
|
146.
|
Pieces of land given to knights as payment
|
|
|
147.
|
Worker who was tied to the land
|
|
|
148.
|
A large estate owned by a knight or lord
|
|
|
149.
|
A code of honorable behavior
|
|
|
150.
|
A small farmer who did not own land
|
Other
|
|
|
151.
|
 What is the only completely true statement that
Calvin’s dad makes in this comic?
|